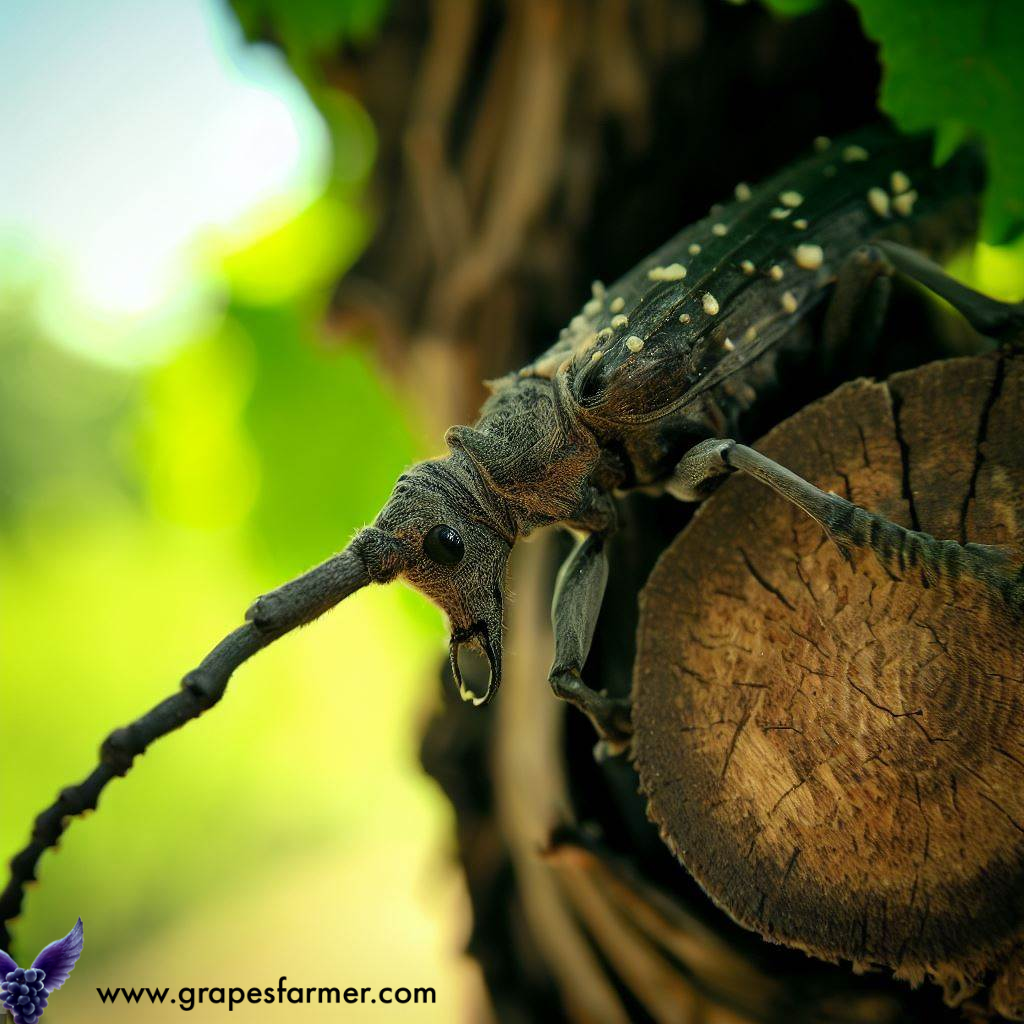
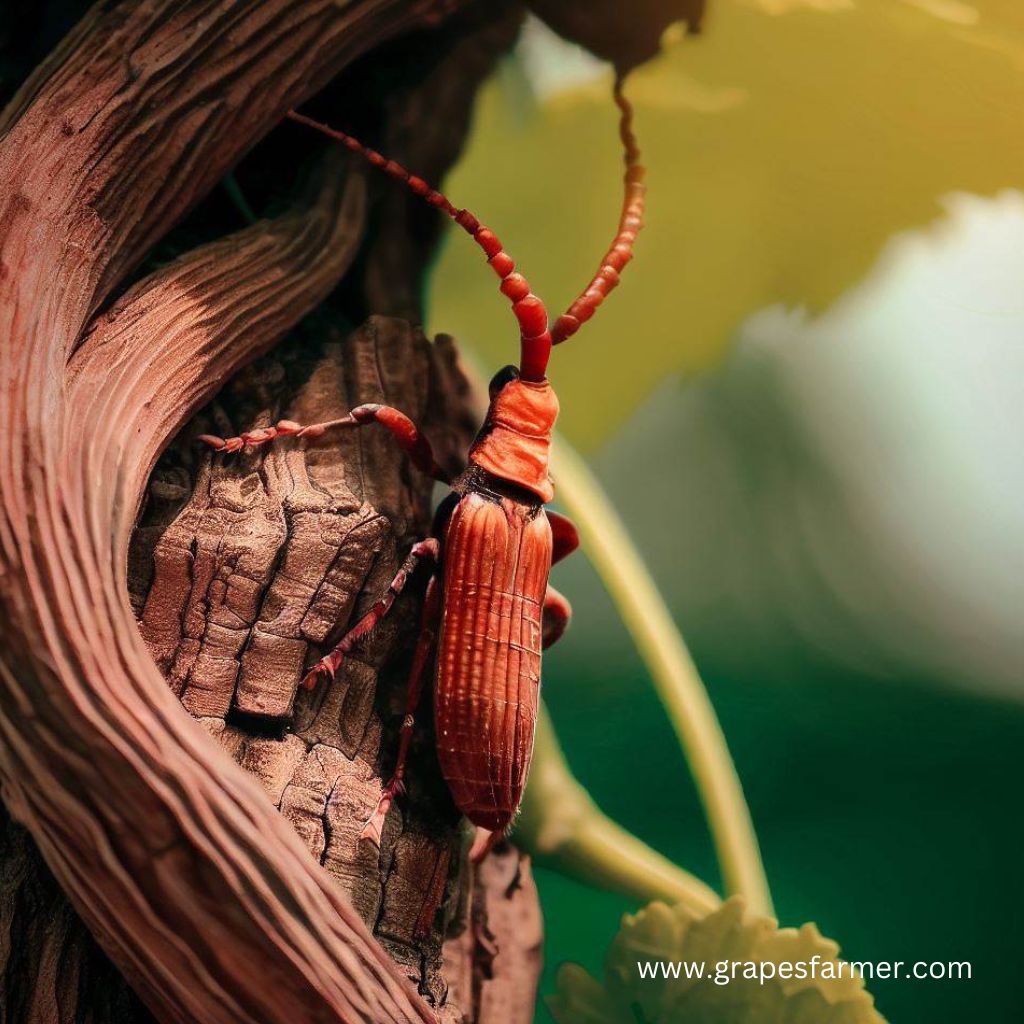
A stem borer is a type of insect that belongs to the order Lepidoptera, which includes moths and butterflies. Stem borers are specifically known for their destructive feeding habits, as their larvae bore into the stems of various plants and cause significant damage. The larvae, commonly referred to as borers, tunnel into the plant’s stems and feed on the internal tissues, disrupting the transport of water and nutrients within the plant.
Stem borers are a major concern for agricultural crops, particularly grains like corn, rice, sugarcane, and sorghum, as well as various other plants. The damage caused by stem borers can result in reduced yields, weakened plants, and sometimes even complete crop loss if the infestation is severe.
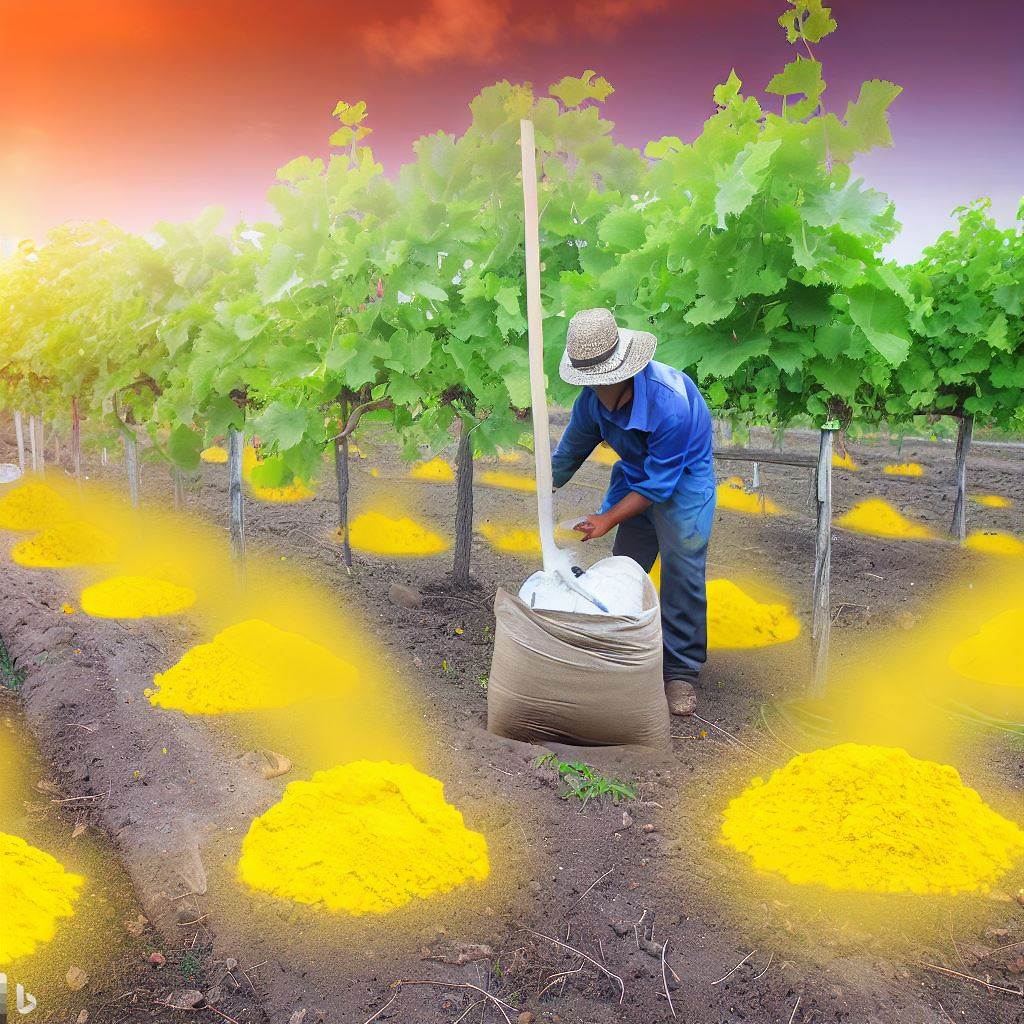
Farmers and agricultural researchers employ various methods to control stem borers, including biological control agents, cultural practices, and chemical pesticides. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies are often used to minimize the impact of stem borers while reducing environmental risks associated with excessive pesticide use.
It’s worth noting that there are various species of stem borers, and they may differ in their appearance, behavior, and preferred host plants. Effective identification of the specific stem borer species is crucial for implementing targeted control measures.